

Also, when sunlight passes through trees, they are diffracted because trees are obstacles in the path of sunlight. The sun appears red because light gets diffracted in the presence of dust particles in the atmosphere.

Hologram projection is also an example of diffraction.These pits have the same width and are equally spaced in a row, forming a diffraction grating on the CD mirror surface. Recorded data on CD is stored in tiny pits of different lengths, which carry the information. Another example of diffraction is while observing the back of a compact disc (CD).The diffraction of sunlight by clouds is a common phenomenon referred to as a silver lining. Diffracted light bends around atmospheric particles like tiny water droplets that are present in clouds producing light and dark fringes or colored bands. Diffraction Meaning: It is the process by which a stream of light or wave is spread out as a result of passing via a narrow area or across an edge. An example of diffraction is seen in the atmosphere. It provides angular dispersion, i.e., the ability to separate wavelengths based on the angle that they emerge from the grating.There are two types of diffraction: Fresnel diffraction and Fraunhofer diffraction.
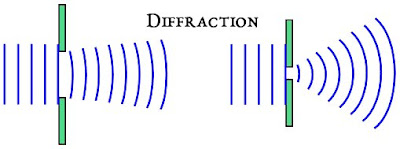
Diffraction experiments have shown that light has wavelike properties.ĭiffraction experiments can be performed with one slit ( single-slit diffraction), two slits ( double-slit diffraction), or multiple slits (diffraction grating). A change of media is required for refraction to take place. X-ray diffraction is a popular technique to discover the structures of organic molecules such as proteins ( Session 31) and, most famously, DNA ( Session 32 ), as well as inorganic crystals. A bright central fringe is observed at the center, surrounded by several maxima and minima. Diffraction is the spreading of light when it passes through a narrow opening or around an object. This shift will cause the wave to have interference with itself. It consists of alternating dark and bright fringes spread across the screen. Diffraction is caused by one wave of light being shifted by a diffracting object. The diffracted waves fall a screen and form a pattern known as a diffraction pattern. Due to diffraction, the direction of waves changes as they pass around an obstacle in their path.Īccording to Huygens’ principle, the aperture or slit diffracting the waves becomes the secondary source of waves. In physics, diffraction is a change in the direction of a sound wave or a light wave caused by the presence of an obstacle in its path.the diffraction of.

The bending will be almost unnoticeable if the opening is much larger than the wavelength. The amount of bending depends on the relative size of the opening compared to the wavelength of light. The obstacle can be an aperture or slit whose size is approximately the same as the wavelength of light. We now consider another way that such a direction change can occur. For example, waves travel faster in deep water than in shallow. Refraction We saw that light waves have the capability of changing the direction of the rays associated with it through diffraction. However, the effect is still there, and there is a diffraction limit to what is observable.Diffraction is the bending or spreading of light waves around an obstacle. refraction, in physics, the change in direction of a wave passing from one medium to another caused by its change in speed. As noticed, diffraction effects are most noticeable when light interacts with objects having sizes on the order of the wavelength of light. The angle found in part (a) is extraordinarily small (less than 1/50,000 of a degree), because the primary mirror is so large compared with the wavelength of light.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
